GPT-NeoX
This model was released on 2022-04-14 and added to Hugging Face Transformers on 2022-05-24.
GPT-NeoX
Section titled “GPT-NeoX”

Overview
Section titled “Overview”We introduce GPT-NeoX-20B, a 20 billion parameter autoregressive language model trained on the Pile, whose weights will be made freely and openly available to the public through a permissive license. It is, to the best of our knowledge, the largest dense autoregressive model that has publicly available weights at the time of submission. In this work, we describe GPT-NeoX-20B’s architecture and training and evaluate its performance on a range of language-understanding, mathematics, and knowledge-based tasks. We find that GPT-NeoX-20B is a particularly powerful few-shot reasoner and gains far more in performance when evaluated five-shot than similarly sized GPT-3 and FairSeq models. We open-source the training and evaluation code, as well as the model weights, at https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neox.
Development of the model was led by Sid Black, Stella Biderman and Eric Hallahan, and the model was trained with generous the support of CoreWeave.
GPT-NeoX-20B was trained with fp16, thus it is recommended to initialize the model as follows:
model = GPTNeoXForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neox-20b", device_map="auto", dtype=torch.float16)GPT-NeoX-20B also has a different tokenizer from the one used in GPT-J-6B and GPT-Neo. The new tokenizer allocates additional tokens to whitespace characters, making the model more suitable for certain tasks like code generation.
Usage example
Section titled “Usage example”The generate() method can be used to generate text using GPT Neo model.
>>> from transformers import GPTNeoXForCausalLM, GPTNeoXTokenizerFast
>>> model = GPTNeoXForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neox-20b")>>> tokenizer = GPTNeoXTokenizerFast.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neox-20b")
>>> prompt = "GPTNeoX20B is a 20B-parameter autoregressive Transformer model developed by EleutherAI."
>>> input_ids = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids
>>> gen_tokens = model.generate(... input_ids,... do_sample=True,... temperature=0.9,... max_length=100,... )>>> gen_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(gen_tokens)[0]Using Flash Attention 2
Section titled “Using Flash Attention 2”Flash Attention 2 is an faster, optimized version of the model.
Installation
Section titled “Installation”First, check whether your hardware is compatible with Flash Attention 2. The latest list of compatible hardware can be found in the official documentation.
Next, install the latest version of Flash Attention 2:
pip install -U flash-attn --no-build-isolationTo load a model using Flash Attention 2, we can pass the argument attn_implementation="flash_attention_2" to .from_pretrained. We’ll also load the model in half-precision (e.g. torch.float16), since it results in almost no degradation to audio quality but significantly lower memory usage and faster inference:
>>> from transformers import GPTNeoXForCausalLM, GPTNeoXTokenizerFast
model = GPTNeoXForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neox-20b", dtype=torch.float16, attn_implementation="flash_attention_2").to(device)...Expected speedups
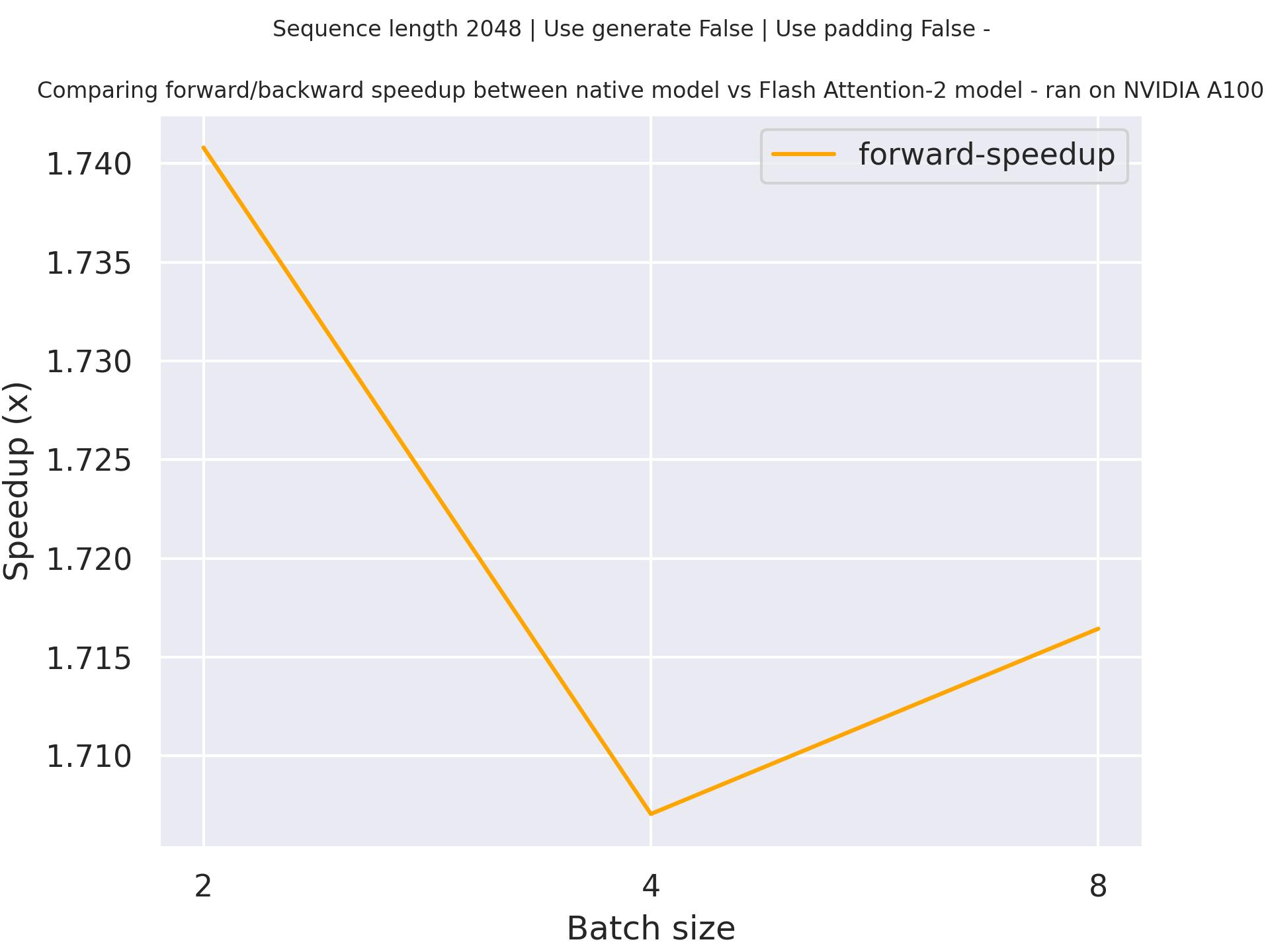
Section titled “Expected speedups”Below is an expected speedup diagram that compares pure inference time between the native implementation in transformers using stockmark/gpt-neox-japanese-1.4b checkpoint and the Flash Attention 2 version of the model using a sequence length of 2048.
Using Scaled Dot Product Attention (SDPA)
Section titled “Using Scaled Dot Product Attention (SDPA)”PyTorch includes a native scaled dot-product attention (SDPA) operator as part of torch.nn.functional. This function
encompasses several implementations that can be applied depending on the inputs and the hardware in use. See the
official documentation
or the GPU Inference
page for more information.
SDPA is used by default for torch>=2.1.1 when an implementation is available, but you may also set
attn_implementation="sdpa" in from_pretrained() to explicitly request SDPA to be used.
from transformers import GPTNeoXForCausalLMmodel = GPTNeoXForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neox-20b", dtype=torch.float16, attn_implementation="sdpa")...For the best speedups, we recommend loading the model in half-precision (e.g. torch.float16 or torch.bfloat16).
On a local benchmark (rtx3080ti-16GB, PyTorch 2.2.1, OS Ubuntu 22.04) using float16 with
pythia-410m-deduped, we saw the
following speedups during training and inference.
Training
Section titled “Training”| Batch size | Seq len | Time per batch (Eager - s) | Time per batch (SDPA - s) | Speedup (%) | Eager peak mem (MB) | SDPA peak mem (MB) | Mem saving (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 128 | 0.024 | 0.019 | 28.945 | 1789.95 | 1789.95 | 0 |
| 1 | 256 | 0.039 | 0.031 | 23.18 | 1845.83 | 1844.84 | 0.053 |
| 1 | 512 | 0.08 | 0.055 | 45.524 | 2278.38 | 1953.76 | 16.615 |
| 1 | 1024 | 0.19 | 0.102 | 86.777 | 4772.36 | 2408.35 | 98.159 |
| 1 | 2048 | 0.565 | 0.204 | 177.098 | 13484.1 | 3882.01 | 247.348 |
| 2 | 128 | 0.037 | 0.032 | 15.121 | 1843.86 | 1844.78 | -0.05 |
| 2 | 256 | 0.067 | 0.055 | 21.706 | 1999.72 | 1951.67 | 2.462 |
| 2 | 512 | 0.144 | 0.096 | 50.046 | 3613.16 | 2406.77 | 50.125 |
| 2 | 1024 | 0.366 | 0.193 | 89.666 | 8707.55 | 3878.86 | 124.487 |
| 2 | 2048 | OOM | 0.379 | / | OOM | 6825.13 | SDPA does not OOM |
| 4 | 128 | 0.06 | 0.054 | 11.539 | 1947.6 | 1952.06 | -0.228 |
| 4 | 256 | 0.119 | 0.093 | 28.072 | 3008.39 | 2405.99 | 25.038 |
| 4 | 512 | 0.275 | 0.187 | 47.145 | 6290.58 | 3877.29 | 62.242 |
| 4 | 1024 | OOM | 0.36 | / | OOM | 6821.98 | SDPA does not OOM |
| 4 | 2048 | OOM | 0.731 | / | OOM | 12705.1 | SDPA does not OOM |
Inference
Section titled “Inference”| Batch size | Seq len | Per token latency Eager (ms) | Per token latency SDPA (ms) | Speedup (%) | Mem Eager (MB) | Mem SDPA (MB) | Mem saved (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 128 | 6.569 | 5.858 | 12.14 | 974.831 | 974.826 | 0 |
| 1 | 256 | 7.009 | 5.863 | 19.542 | 1029.01 | 1028.08 | 0.09 |
| 1 | 512 | 7.157 | 5.965 | 19.983 | 1137.54 | 1137.52 | 0.001 |
| 1 | 1024 | 7.523 | 6.506 | 15.637 | 1329.3 | 1329.26 | 0.003 |
| 1 | 2048 | 9.271 | 9.205 | 0.713 | 1752.47 | 1734.51 | 1.036 |
| 2 | 128 | 7.239 | 5.959 | 21.493 | 1044.8 | 1028.37 | 1.597 |
| 2 | 256 | 7.228 | 6.036 | 19.757 | 1167.32 | 1137.73 | 2.601 |
| 2 | 512 | 7.538 | 6.693 | 12.628 | 1352.93 | 1329.55 | 1.758 |
| 2 | 1024 | 8.916 | 8.632 | 3.291 | 1752.56 | 1734.62 | 1.034 |
| 2 | 2048 | 12.628 | 12.606 | 0.181 | 2558.72 | 2545.8 | 0.508 |
| 4 | 128 | 7.278 | 6.046 | 20.373 | 1168.41 | 1137.79 | 2.691 |
| 4 | 256 | 7.614 | 6.588 | 15.574 | 1353.1 | 1329.79 | 1.753 |
| 4 | 512 | 8.798 | 8.144 | 8.028 | 1752.76 | 1734.85 | 1.032 |
| 4 | 1024 | 11.765 | 11.303 | 4.09 | 2558.96 | 2546.04 | 0.508 |
| 4 | 2048 | 19.568 | 17.735 | 10.33 | 4175.5 | 4165.26 | 0.246 |
Resources
Section titled “Resources”GPTNeoXConfig
Section titled “GPTNeoXConfig”[[autodoc]] GPTNeoXConfig
GPTNeoXTokenizer
Section titled “GPTNeoXTokenizer”[[autodoc]] GPTNeoXTokenizer
GPTNeoXTokenizerFast
Section titled “GPTNeoXTokenizerFast”[[autodoc]] GPTNeoXTokenizerFast
GPTNeoXModel
Section titled “GPTNeoXModel”[[autodoc]] GPTNeoXModel - forward
GPTNeoXForCausalLM
Section titled “GPTNeoXForCausalLM”[[autodoc]] GPTNeoXForCausalLM - forward
GPTNeoXForQuestionAnswering
Section titled “GPTNeoXForQuestionAnswering”[[autodoc]] GPTNeoXForQuestionAnswering - forward
GPTNeoXForSequenceClassification
Section titled “GPTNeoXForSequenceClassification”[[autodoc]] GPTNeoXForSequenceClassification - forward
GPTNeoXForTokenClassification
Section titled “GPTNeoXForTokenClassification”[[autodoc]] GPTNeoXForTokenClassification - forward