Csm
This model was released on 2025-02-27 and added to Hugging Face Transformers on 2025-05-07.
Overview
Section titled “Overview”The Conversational Speech Model (CSM) is the first open-source contextual text-to-speech model released by Sesame. It is designed to generate natural-sounding speech with or without conversational context. This context typically consists of multi-turn dialogue between speakers, represented as sequences of text and corresponding spoken audio.
Model Architecture: CSM is composed of two LLaMA-style auto-regressive transformer decoders: a backbone decoder that predicts the first codebook token and a depth decoder that generates the remaining tokens. It uses the pretrained codec model Mimi, introduced by Kyutai, to encode speech into discrete codebook tokens and decode them back into audio.
The original csm-1b checkpoint is available under the Sesame organization on Hugging Face.
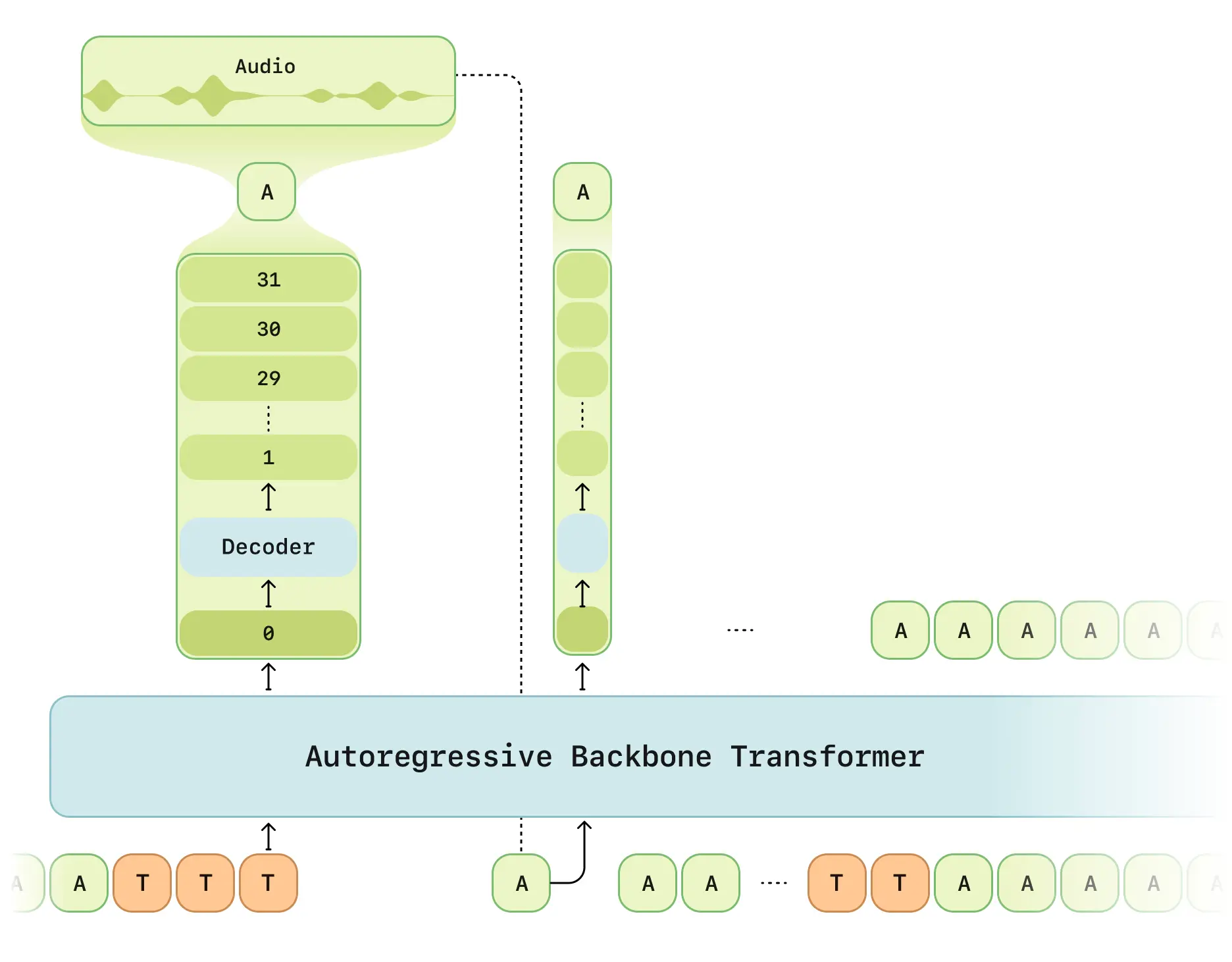
Usage Tips
Section titled “Usage Tips”Without Conversational Context
Section titled “Without Conversational Context”CSM can be used to simply generate speech from a text prompt:
import torchfrom transformers import CsmForConditionalGeneration, AutoProcessorfrom accelerate import Accelerator
model_id = "sesame/csm-1b"device = Accelerator().device
# load the model and the processorprocessor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)model = CsmForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map=device)
# prepare the inputstext = "[0]The past is just a story we tell ourselves." # `[0]` for speaker id 0inputs = processor(text, add_special_tokens=True).to(device)
# another equivalent way to prepare the inputsconversation = [ {"role": "0", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": "The past is just a story we tell ourselves."}]},]inputs = processor.apply_chat_template( conversation, tokenize=True, return_dict=True,).to(model.device)
# infer the modelaudio = model.generate(**inputs, output_audio=True)processor.save_audio(audio, "example_without_context.wav")With Conversational Context
Section titled “With Conversational Context”CSM can be used to generate speech given a conversation, allowing consistency in the voices and content-aware generation:
import torchfrom transformers import CsmForConditionalGeneration, AutoProcessorfrom accelerate import Acceleratorfrom datasets import load_dataset, Audio
model_id = "sesame/csm-1b"device = Accelerator().device
# load the model and the processorprocessor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)model = CsmForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map=device)
# prepare the inputsds = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/dailytalk-dummy", split="train")# ensure the audio is 24kHzds = ds.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=24000))conversation = []
# 1. contextfor text, audio, speaker_id in zip(ds[:4]["text"], ds[:4]["audio"], ds[:4]["speaker_id"]): conversation.append( { "role": f"{speaker_id}", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": text}, {"type": "audio", "path": audio["array"]}], } )
# 2. text promptconversation.append({"role": f"{ds[4]['speaker_id']}", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": ds[4]["text"]}]})
inputs = processor.apply_chat_template( conversation, tokenize=True, return_dict=True,).to(model.device)
# infer the modelaudio = model.generate(**inputs, output_audio=True)processor.save_audio(audio, "example_with_context.wav")Batched Inference
Section titled “Batched Inference”CSM supports batched inference!
import torchfrom transformers import CsmForConditionalGeneration, AutoProcessorfrom accelerate import Acceleratorfrom datasets import load_dataset, Audio
model_id = "sesame/csm-1b"device = Accelerator().device
# load the model and the processorprocessor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)model = CsmForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map=device)
# prepare the inputsds = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/dailytalk-dummy", split="train")# ensure the audio is 24kHzds = ds.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=24000))# here a batch with two promptsconversation = [ [ { "role": f"{ds[0]['speaker_id']}", "content": [ {"type": "text", "text": ds[0]["text"]}, {"type": "audio", "path": ds[0]["audio"]["array"]}, ], }, { "role": f"{ds[1]['speaker_id']}", "content": [ {"type": "text", "text": ds[1]["text"]}, ], }, ], [ { "role": f"{ds[0]['speaker_id']}", "content": [ {"type": "text", "text": ds[0]["text"]}, ], } ],]inputs = processor.apply_chat_template( conversation, tokenize=True, return_dict=True,).to(model.device)
audio = model.generate(**inputs, output_audio=True)processor.save_audio(audio, [f"speech_batch_idx_{i}.wav" for i in range(len(audio))])Making The Model Go Brrr
Section titled “Making The Model Go Brrr”CSM supports full-graph compilation with CUDA graphs!
import torchimport copyfrom transformers import CsmForConditionalGeneration, AutoProcessorfrom datasets import load_dataset
model_id = "sesame/csm-1b"device = "cuda"
# set logs to ensure no recompilation and graph breakstorch._logging.set_logs(graph_breaks=True, recompiles=True, cudagraphs=True)
# load the model and the processorprocessor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)model = CsmForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map=device)
# use static cache, enabling automatically torch compile with fullgraph and reduce-overheadmodel.generation_config.max_length = 250 # big enough to avoid recompilationmodel.generation_config.max_new_tokens = None # would take precedence over max_lengthmodel.generation_config.cache_implementation = "static"model.depth_decoder.generation_config.cache_implementation = "static"
# generation kwargsgen_kwargs = { "do_sample": False, "depth_decoder_do_sample": False, "temperature": 1.0, "depth_decoder_temperature": 1.0,}
# Define a timing decoratorclass TimerContext: def __init__(self, name="Execution"): self.name = name self.start_event = None self.end_event = None
def __enter__(self): # Use CUDA events for more accurate GPU timing self.start_event = torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True) self.end_event = torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True) self.start_event.record() return self
def __exit__(self, *args): self.end_event.record() torch.cuda.synchronize() elapsed_time = self.start_event.elapsed_time(self.end_event) / 1000.0 print(f"{self.name} time: {elapsed_time:.4f} seconds")
# prepare the inputsds = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/dailytalk-dummy", split="train")
conversation = [ { "role": f"{ds[0]['speaker_id']}", "content": [ {"type": "text", "text": ds[0]["text"]}, {"type": "audio", "path": ds[0]["audio"]["array"]}, ], }, { "role": f"{ds[1]['speaker_id']}", "content": [ {"type": "text", "text": ds[1]["text"]}, {"type": "audio", "path": ds[1]["audio"]["array"]}, ], }, { "role": f"{ds[2]['speaker_id']}", "content": [ {"type": "text", "text": ds[2]["text"]}, ], },]
padded_inputs_1 = processor.apply_chat_template( conversation, tokenize=True, return_dict=True,).to(model.device)
print("\n" + "="*50)print("First generation - compiling and recording CUDA graphs...")with TimerContext("First generation"): _ = model.generate(**padded_inputs_1, **gen_kwargs)print("="*50)
print("\n" + "="*50)print("Second generation - fast !!!")with TimerContext("Second generation"): _ = model.generate(**padded_inputs_1, **gen_kwargs)print("="*50)
# now with different inputsconversation = [ { "role": f"{ds[0]['speaker_id']}", "content": [ {"type": "text", "text": ds[2]["text"]}, {"type": "audio", "path": ds[2]["audio"]["array"]}, ], }, { "role": f"{ds[1]['speaker_id']}", "content": [ {"type": "text", "text": ds[3]["text"]}, {"type": "audio", "path": ds[3]["audio"]["array"]}, ], }, { "role": f"{ds[2]['speaker_id']}", "content": [ {"type": "text", "text": ds[4]["text"]}, ], },]padded_inputs_2 = processor.apply_chat_template( conversation, tokenize=True, return_dict=True,).to(model.device)
print("\n" + "="*50)print("Generation with other inputs!")with TimerContext("Generation with different inputs"): _ = model.generate(**padded_inputs_2, **gen_kwargs)print("="*50)Training
Section titled “Training”CSM Transformers integration supports training!
from transformers import CsmForConditionalGeneration, AutoProcessorfrom accelerate import Acceleratorfrom datasets import load_dataset, Audio
model_id = "sesame/csm-1b"device = Accelerator().device
# load the model and the processorprocessor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)model = CsmForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map=device)model.train()model.codec_model.eval()
ds = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/dailytalk-dummy", split="train")# ensure the audio is 24kHzds = ds.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=24000))conversation = []
# contextfor text, audio, speaker_id in zip(ds[:4]["text"], ds[:4]["audio"], ds[:4]["speaker_id"]): conversation.append( { "role": f"{speaker_id}", "content": [{"type": "text", "text": text}, {"type": "audio", "path": audio["array"]}], } )
inputs = processor.apply_chat_template( conversation, tokenize=True, return_dict=True, output_labels=True,).to(model.device)
out = model(**inputs)out.loss.backward()This model was contributed by Eustache Le Bihan. The original code can be found here.
CsmConfig
Section titled “CsmConfig”[[autodoc]] CsmConfig
CsmDepthDecoderConfig
Section titled “CsmDepthDecoderConfig”[[autodoc]] CsmDepthDecoderConfig
CsmProcessor
Section titled “CsmProcessor”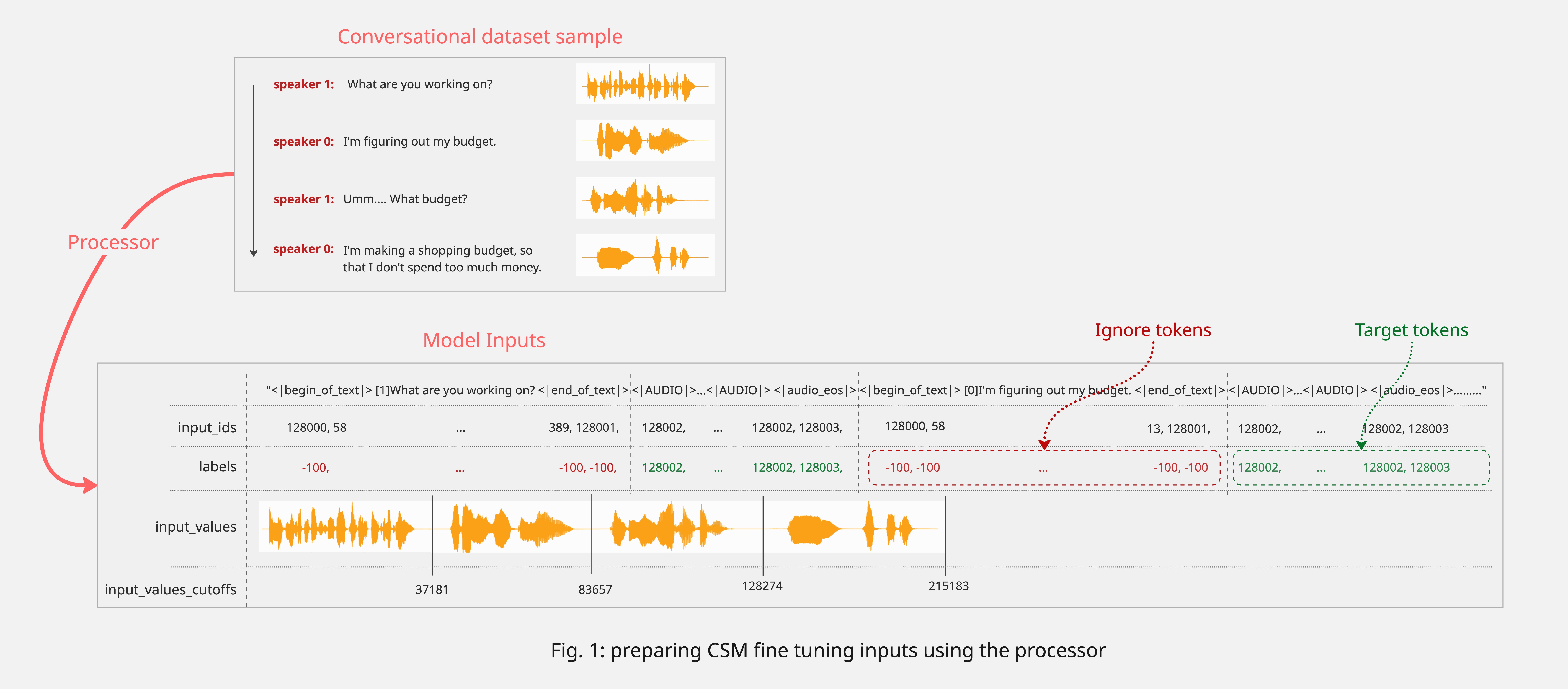
[[autodoc]] CsmProcessor - call
CsmForConditionalGeneration
Section titled “CsmForConditionalGeneration”[[autodoc]] CsmForConditionalGeneration - forward - generate
CsmDepthDecoderForCausalLM
Section titled “CsmDepthDecoderForCausalLM”[[autodoc]] CsmDepthDecoderForCausalLM
CsmDepthDecoderModel
Section titled “CsmDepthDecoderModel”[[autodoc]] CsmDepthDecoderModel
CsmBackboneModel
Section titled “CsmBackboneModel”[[autodoc]] CsmBackboneModel